Linux command tutorials like you share common Linux commands, syntax and use cases, and will not list the options and parameters of each command in detail.
Linux Commands Tutorial
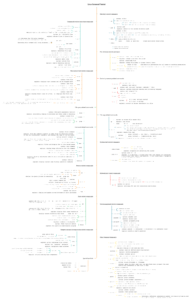
1. Linux common directory command list
linux cd command
- explain:
switch directory
- syntax
cd dir- case
In the following example we will switch to the previous directory.
cd - : switch to the previous directoryIn the following example we will switch to the user root directory.
cd (~) : switch to the user root directorylinux pwd command
- explain
return to the current directory path
- syntax
pwdlinux ls command
- explain
list directories and files under dir
- syntax
ls dir- case
ls -a DIR : list all directories and files, including. * fileslinux mkdir command
- explain
make directories
- syntax
mkdir dir- case
mkdir -p /path/dir : create multilevel directorieslinux rmdir command
- explain
remove directories
- synax
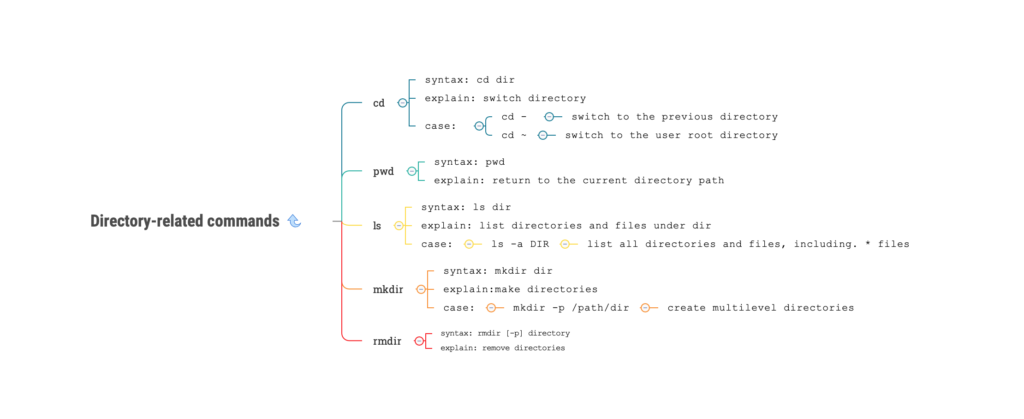
rmdir [-p] directory2. Linux file operations commands
linux touch command
- explain
change file timestamps
- syntax
touch filelinux vim command
- explain
open a file and enter “:wq” or “:x” to hold the file
- syntax
vim/vi filelinux rm command
- explain
delete files or directories
- syntax
rm file- bad case
rm -rf /
rm -rf *
rm -rf ~
-r: indicates the following together;
-f: means no user confirmation required;linux file command
- explain
determine file type
- syntax
file filelinux mv command
- explain
move [rename] files or directories
- syntax
mv source target
linux ln/link command
- explain
make links
- syntax
link source_file target_file
linux unlink command
- explain
remove directory entries
- syntax
unlink file
linux lsof command
- explain
list open files
- syntax
lsof names
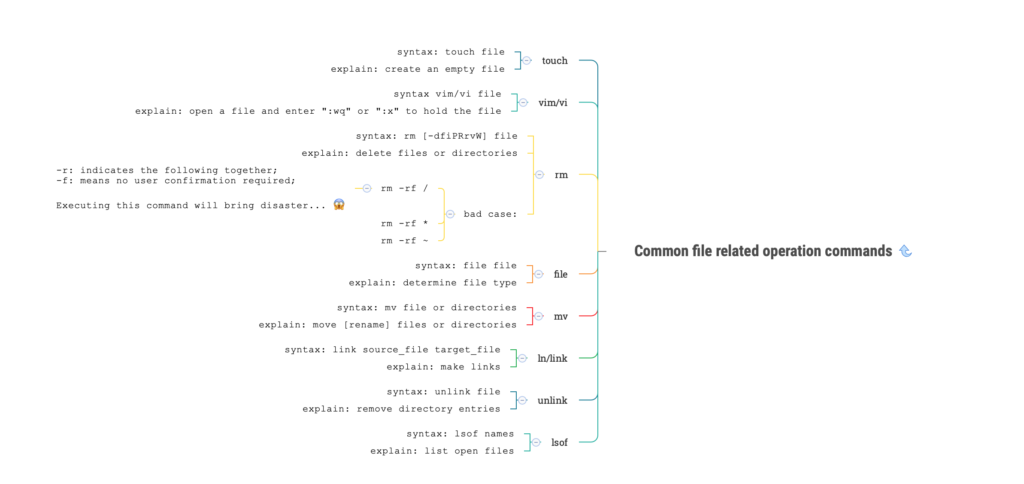
3. Linux file permissions commands
linux chown command
- explain
change file owner and group
- syntax
chown owner[:group] file
linux chmod command
- explain
change file modes or Access Control Lists
- syntax
chmod mode file
- case
chmod +x file : add execution permissions for all users to existing permissions
chmod 777 file : give file owners read, write, and execute permissionslinux chgrp command
- explain:
change group
- syntax:
chgrp group file
4. Linux file content view commands
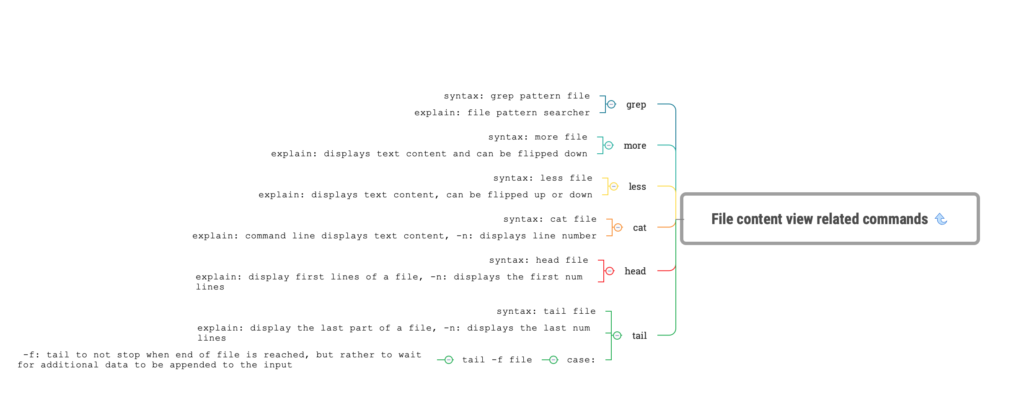
linux grep command
- explain:
file pattern searcher
- syntax:
grep pattern file
linux more command
- explain:
displays text content and can be flipped down
- syntax:
more file
linux less command
- explain:
displays text content, can be flipped up or down
- syntax:
less file
linux cat command
- explain:
command line displays text content, -n: displays line number
- syntax:
cat file
linux head command
- explain:
display first lines of a file, -n: displays the first num lines
- syntax:
head file
linux tail command
- explain:
display the last part of a file, -n: displays the last num lines
- syntax:
tail file
- case:
In the following example we will get the last 10 lines of the file file.log and the new content as they get appended to the file.
tail -f file.log
-f: tail to not stop when end of file is reached, but rather to wait for additional data to be appended to the input5. Linux text processing commands
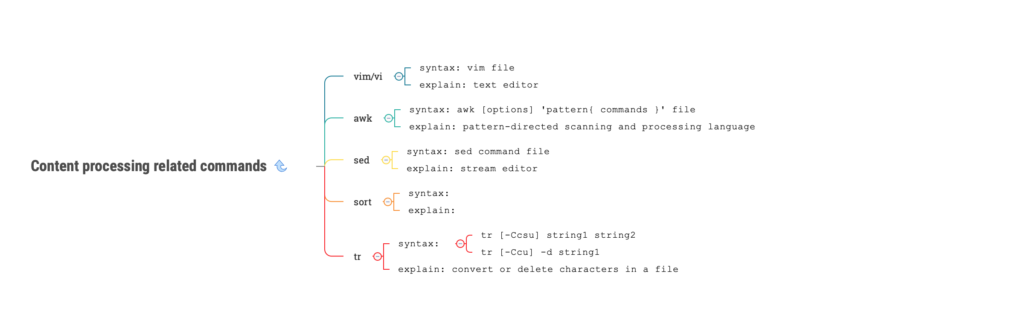
linux vim/vi command
- explain:
text editor
- syntax:
vim file
linux awk command
- explain:
pattern-directed scanning and processing language
- syntax:
awk [options] ‘pattern{ commands }’ file
linux sed command
- explain:
stream editor
- syntax:
sed command file
linux sort command
- explain:
sort or merge records (lines) of text and binary files
- syntax:
sort
linux tr command
- explain:
convert or delete characters in a file
- syntax:
tr [-Ccsu] string1 string2
tr [-Ccu] -d string1
6. Linux file query related commands
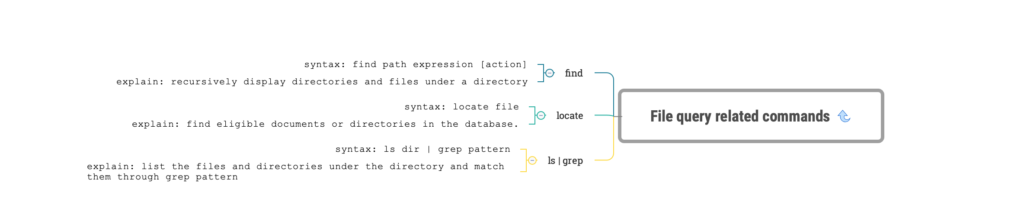
linux find command
- explain:
recursively display directories and files under a directory
- syntax:
find path expression [action]
linux locate command
- explain:
find eligible documents or directories in the database.
- syntax:
locate file
linux ls|grep command
- explain:
list the files and directories under the directory and match them through grep pattern
- syntax:
ls dir | grep pattern
7. Linux file copy related commands
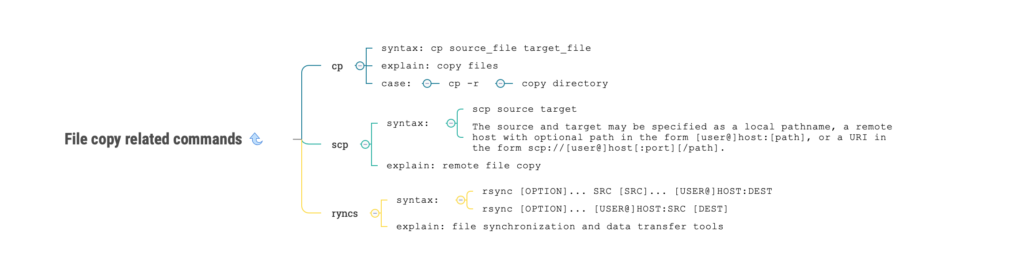
linux cp command
- explain:
copy files
- syntax:
cp source_file target_file
- case:
cp -r : copy directory
linux scp command
- explain:
remote file copy;The source and target may be specified as a local pathname, a remote host with optional path in the form [user@]host:[path], or a URI in the form scp://[user@]host[:port][/path].
- syntax:
scp source target
linux syncs command
- explain:
file synchronization and data transfer tools
- syntax
rsync [OPTION]... SRC [SRC]... [USER@]HOST:DEST
rsync [OPTION]... [USER@]HOST:SRC [DEST]8. Command related commands
linux which command
- explain:
find the command location in order from the directory listed in the Path environment variable, and display the name of the full path
- syntax:
which command
linux whereis command
- explain:
Find out the executable file, source code file and the path of manpage for a particular program.
- syntax:
whereis command
linux man command
- explain:
format and display the on-line manual pages
- syntax:
man command
linux help command
- explain:
display help information for the command
- syntax:
help command
linux alias command
- explain:
set the alias of the command
- syntax:
alias [alias]=[command name]
linux sudo command
- explain:
allow an authorized user to run a command as superuser or other user
- syntax:
sudo commands
linux history command
- explain:
display current user history operation commands
- syntax:
history
9. System related commands
reboot/halt
syntax:
halt [-lnqu]
reboot [-lnq]
explain: stopping and restarting the system
init 0-6
syntax: init [0 - 6]
explain: 0 is shutdown, 1 single user mode (can change root password), 2 multi-user mode (cannot use network), 3 full multi-user, 4 graphics, 5 security mode, 6 restart
shutdown
syntax: shutdown time
explain: close down the system at a given time10. Process related commands
linux ps command
- explain:
process status
- syntax:
ps option
- case:
In the following example we will list the running system processes.
ps -ef
: list current system processesIn the following example query whether the system is running the process.
ps -ef | grep xxx
: whether the query process is executinglinux kill command
- explain:
terminate or signal a process
- syntax:
kill pid
kill -signal_number pid- case:
kill -9 pid : forced killing processlinux killall command
syntax: killall procname
explain: kill processes by namelinux top command
- explain
display and update sorted information about processes
- syntax
top option11. Network/port related commands
netstat
syntax: netstat option
explain: show network status
case:
netstat -anp | grep 80
:view port 80 information
nc
syntax: nc option
explain: arbitrary TCP and UDP connections and listens12. Disk related commands
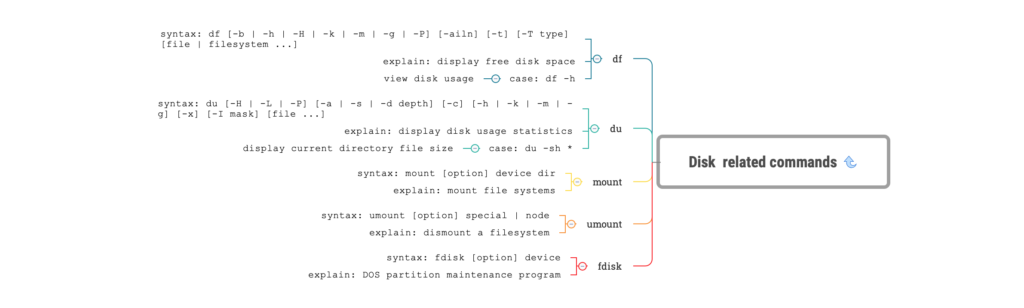
df
syntax: df [-b | -h | -H | -k | -m | -g | -P] [-ailn] [-t] [-T type] [file | filesystem ...]
explain: display free disk space
case:
df -h : view disk usage
du
syntax: du [-H | -L | -P] [-a | -s | -d depth] [-c] [-h | -k | -m | -g] [-x] [-I mask] [file ...]
explain: display disk usage statistics
case:
du -sh *
:display current directory file size
mount
syntax: mount [option] device dir
explain: mount file systems
umount
syntax: umount [option] special | node
explain: dismount a filesystem
fdisk
syntax: fdisk [option] device
explain: DOS partition maintenance program13. User management related commands
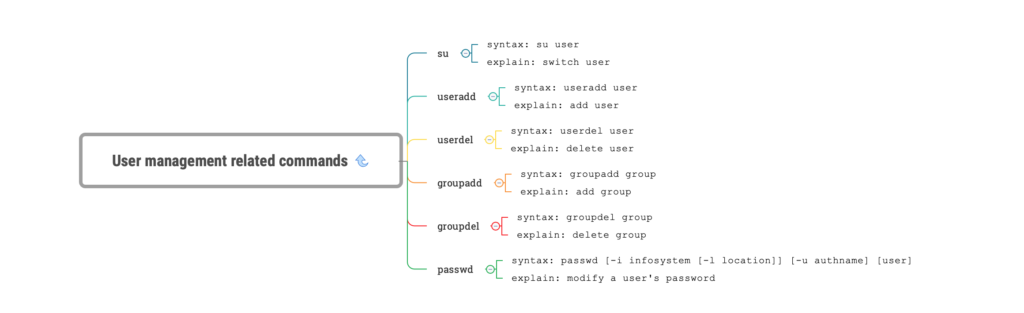
su
syntax: su user
explain: switch user
useradd
syntax: useradd user
explain: add user
userdel
syntax: userdel user
explain: delete user
groupadd
syntax: groupadd group
explain: add group
groupdel
syntax: groupdel group
explain: delete group
passwd
syntax: passwd [-i infosystem [-l location]] [-u authname] [user]
explain: modify a user's password14. Compression and decompression related commands
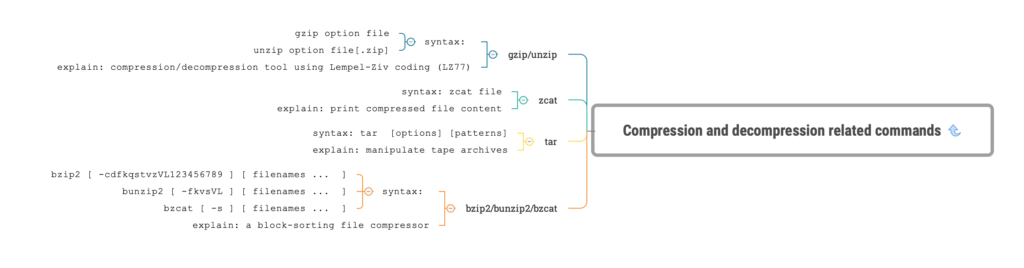
gzip/unzip
syntax:
gzip option file
unzip option file[.zip]
explain: compression/decompression tool using Lempel-Ziv coding (LZ77)
zcat
syntax: zcat file
explain: print compressed file content
tar
syntax: tar [options] [patterns]
explain: manipulate tape archives
bzip2/bunzip2/bzcat
syntax:
bzip2 [ -cdfkqstvzVL123456789 ] [ filenames ... ]
bunzip2 [ -fkvsVL ] [ filenames ... ]
bzcat [ -s ] [ filenames ... ]
explain: a block-sorting file compressor15. Other Common Commands

linux crontab command
- explain:
service management
- syntax:
crontab option
uname
syntax: uname [-amnprsv]
explain: print operating system name
date
syntax: date option
explain: display or set date and time
service
syntax: service SERVICE start/stop/restart
explain: service management
wc
syntax: wc [-clmw] [file ...]
explain: word, line, character, and byte count
source
syntax: source filename or .filename
explain: make the shell read into the specified shell program file and execute all statements in the file in turn
w
syntax: w [option]
explain: display who is logged in and what they are doing
echo
syntax: echo [option]
explain: write arguments to the standard output
print
syntax: print contents
explain: print contents
printf
syntax: printf format [arguments ...]
explain: format printed content
case:
printf "Distance is %5d Miles\n" $d
ssh
syntax: ssh [option] destination [command]
explain: OpenSSH SSH client
ulimit
syntax: ulimit [option]
explain: view system limit
case:
ulimit -a
:view current limit
ulimit -n 65535
:temporary, effective immediately;modify /etc/security/limits.conf file, permanently effective modifications.16. Special symbols
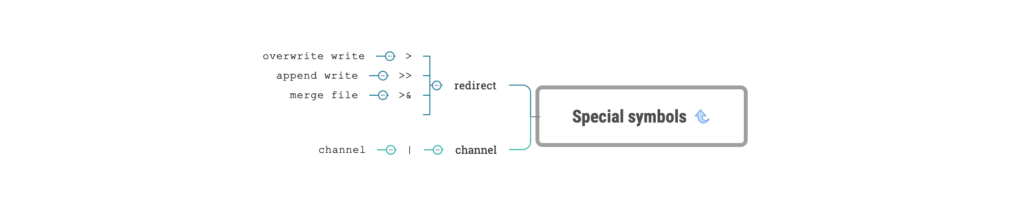
redirect
“>” symbol, left content overwrite to right file
“>>” symbol, the content on the left is appended to the end of the file on the right
>
:overwrite write
>>
:append write
pipe
|
: pipe