After the login system, under the command window type the command:
ls /You will see as shown in the figure below:
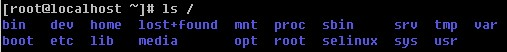
Tree directory structure:
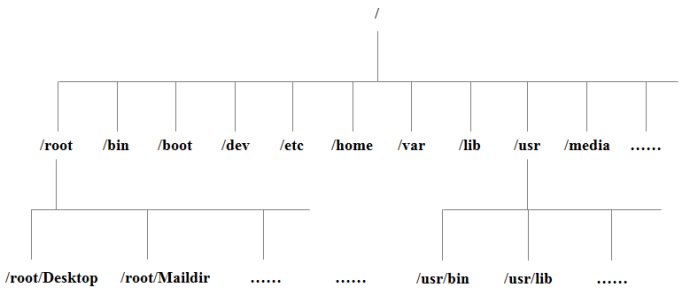
The following is the explanation for these directories:
/bin:
Bin is the abbreviation of Binary, this directory holds the most frequently used commands.
/boot:
Store here are some of the core files used boot Linux, including some connection file and image file.
/dev:
Dev is Device (equipment), the directory to store the Linux peripheral equipment, access Device in Linux is the same way and access to the file.
/etc:
This directory is used to store all the systems management need configuration files and subdirectories.
/home:
The user’s home directory, in Linux, each user has a own directory, and generally the directory name is named after the user account.
/lib:
This directory holds the system the most basic of dynamically linked Shared libraries, its action is similar to Windows DLL files.Nearly all applications need to use these Shared libraries.
/lost + found:
This directory is empty, generally after the illegal shutdown system, where some files here.
/media:
Linux system will automatically identify some equipment, such as U disk, cd-rom, etc., after the identification, Linux will reduce the recognition device mounted to the directory.
/mnt:
System to provide the directory is to allow user temporary mount the file system, we can drive mounted on the/MNT /, and then enter the directory can view the content in the optical drive.
/opt:
This is for the host to install additional software directory.For example, if you install an ORACLE databases can into this directory.The default is empty.
/proc:
This directory is a virtual directory, it is the system memory mapping, we could be obtained by direct access to the directory system information. The contents of this directory is not on your hard disk but in memory, we can also directly modify some of the files in it, such as by shielding host ping command, the following command to make someone unable to ping your machine: echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/icmp_echo_ignore_all
/root:
The directory for the system administrator, also known as the super user home directory permissions.
/sbin:
S is the meaning of the Super User, store here is that the system administrator USES system management program.
/selinux:
This directory is peculiar to the Redhat/CentOS directory, Selinux is a security mechanism, similar to Windows firewall, but the mechanism is complicated, the directory is where Selinux related files.
/srv:
The directory to store some after the service need to extract the data.
/sys:
That there is the kernel of a big change.The directory to install the 2.6 kernel new a sysfs file system.
Sysfs file system integrates the following 3 kinds of file system information: proc file system for process information, in view of the equipment would file system and the pseudo terminal devpts file system.
The file system is the kernel equipment a direct reflection of the tree.
When a kernel object is created, the corresponding files and directories in the subsystem of the kernel object is created.
/tmp:
This directory is used to store temporary files.
/usr:
This is a very important directory, the user of the many applications and files in this directory, similar to the Windows program files directory.
/usr/bin:
Users of the system using the application.
/usr/sbin:
Super users to use more advanced management program and system daemon.
/usr/src:
The placement of the kernel source code default directory.
/var:
This directory to deposit in the constantly expanding, we are used to those who are often modified directory in the directory.Including all kinds of log file.
/run:
Is a temporary file system, since the launch of information storage systems.
In a Linux system, there are several directory is more important, at ordinary times need to be careful not to delete or change the internal file by mistake.
/etc: also mentioned above, this is the configuration file in system, if you change a file under this directory may cause system can’t start.
/bin, /sbin, /usr/bin, /usr/sbin: the placement of this is the default file system directory, such as ls is in/bin/ls directory. It should be noted that: /bin and /usr/bin is for users of the system using instruction (except for the root user), /sbin and /usr/sbin instructions used to root.
/var: this is a very important directory, system running on a lot of programs, and each program will have corresponding log, and the log was recorded this directory, specifically in/var/log directory, and mail the default place is here.